The LM75 temperature sensor includes a delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter, and a digital overtemperature detector. The host can query the LM75 through its I²C interface to read temperature at any time. The open-drain overtemperature output (OS) sinks current when the programmable temperature limit is exceeded.
The OS output operates in either of two modes, comparator or interrupt. The host controls the temperature at which the alarm is asserted (TOS) and the hysteresis temperature below which the alarm condition is not valid (THYST). Also, the LM75’s TOS and THYST registers can be read by the host.
The address of the LM75 is set with three pins to allow multiple devices to work on the same bus. Power-up is in comparator mode, with defaults of TOS = +80°C and THYST = +75°C. The 3.0V to 5.5V supply voltage range, low supply current, and I²C interface make the LM75 ideal for many applications in thermal management and protection.
Here is a module that you can buy for this device
Key Features
SO (SOP) and µMAX® (µSOP) Packages
I²C Bus Interface
Separate Open-Drain OS Output Operates as Interrupt or Comparator/Thermostat Input
Register Readback Capability
Power-Up Defaults Permit Stand-Alone Operation as a Thermostat
3.0V to 5.5V Supply Voltage
Low Operating Supply Current 250µA (typ), 1mA (max)
4µA (typ) Shutdown Mode Minimizes Power Consumption
Up to Eight LM75s Can Be Connected to a Single Bus
Parts List
Here are the parts I used
| Name | Links | |
| Wemos Mini | ||
| LM75 | ||
| Connecting cables |
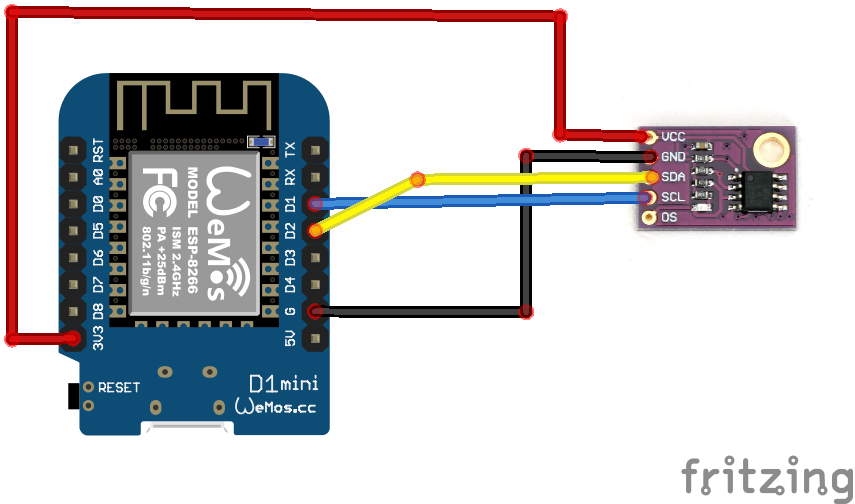
Layout
Being an I2C device you can power it from 3.3 or 5v, in this case we use 3.3v
Code
I used the following library – https://github.com/jlz3008/lm75
#define VERSION "1.1"
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <lm75.h>
TempI2C_LM75 termo = TempI2C_LM75(0x48,TempI2C_LM75::nine_bits);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Start");
Serial.print("Actual temp ");
Serial.print(termo.getTemp());
Serial.println(" oC");
delay(2000);
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print(termo.getTemp());
Serial.println(" oC");
delay(5000);
}
Output
Open the serial monitor and you should see something like this
31.37 oC
30.12 oC
29.37 oC
28.75 oC
28.37 oC
27.87 oC
27.50 oC
27.25 oC
27.00 oC



[…] sicher und stabil angebunden werden. Beispiele sind der digitale LM75 Temperatur-Sensor zur Temperaturmessung oder ein ADS1115 Energiemonitor. Brauchst Du mehr als einen Anschluss, dann wähle […]