In this article we look at another sensor – it is a BMP388 by Bosch Sensortec, so lets crack on and try this out with our Wemos board
As usual we will look at some of the manufacturers information from the website on the sensor
BMP388 Information
The BMP388 is a very small, low-power and low-noise 24 bit absolute barometric pressure sensor. It enables accurate altitude tracking and is specifically suited for drone applications. The best-in-class TCO of the BMP388 between 0-65°C for accurate altitude measurement over a wide temperature range greatly enhances the drone flying experience by making accurate steering easier.
It is compatible for use with other Bosch sensors, including BMI088 for better performance, robustness and stability.
The BMP388 sensor offers outstanding design flexibility, providing a single package solution that is easy to integrate into other existing and upcoming devices such as smart homes, industrial products and wearables.
It is more accurate than its predecessors, covering a wide measurement range from 300 hPa to 1250 hPa. BMP388 exhibits an attractive price-performance ratio coupled with low power consumption. It is available in a compact 10-pin 2.0 x 2.0 x 0.75 mm³ LGA package with metal lid.
- Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V
- Communication interface: I2C/SPI
- Barometric pressure operation range: 300~1250hPa
- Barometric pressure absolute accuracy: ±0.40hPa (@900~1100hPa, 25~40℃)
- Barometric pressure relative accuracy: ±0.08hPa (@900~1100hPa, 25~40℃)
- Temperature coefficient offset: ±0.75Pa/K (@700~1100hPa, -20~65℃))
- Temperature absolute accuracy: ±0.5℃ (0~65℃)
- Possible resolution: 0.016Pa (high precision mode)
- Possible sampling rate: 200Hz
- Operating voltage: -40~85℃
If you purchase a module they will have a 3.3v regulator on board, you will also have the option of I2C or SPI, here is the module that I located. You can see that it has Vin and 3v written on the board
Parts List
Here are the parts I used
| Name | Links | |
| Wemos Mini | ||
| BMP388 | ||
| Connecting cables |
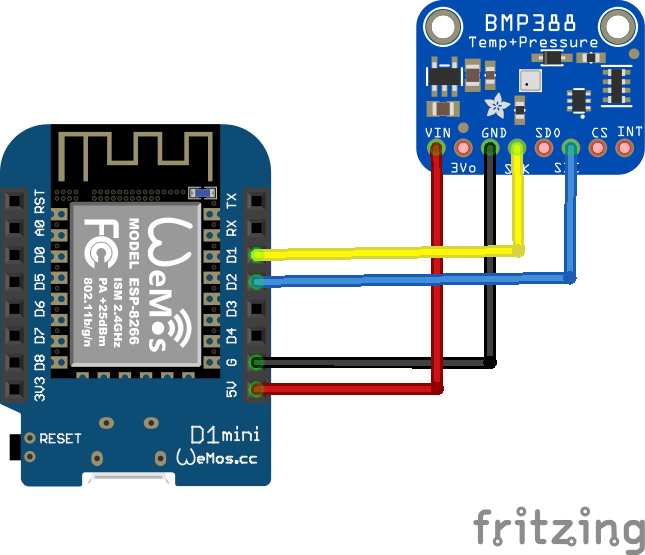
Schematic/Connection
I use the sensor in I2C mode – as you can see in the layout below
Code Example
I used the library from adafruit, you can download this from – https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_BMP3XX.
This library can be installed via the library manager. This is the default code example and I have removed some of the SPI code and code comments since I was using the sensor in I2C mode
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include "Adafruit_BMP3XX.h"
#define SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA (1013.25)
Adafruit_BMP3XX bmp; // I2C
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial);
Serial.println("BMP388 test");
if (!bmp.begin()) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BMP3 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
// Set up oversampling and filter initialization
bmp.setTemperatureOversampling(BMP3_OVERSAMPLING_8X);
bmp.setPressureOversampling(BMP3_OVERSAMPLING_4X);
bmp.setIIRFilterCoeff(BMP3_IIR_FILTER_COEFF_3);
//bmp.setOutputDataRate(BMP3_ODR_50_HZ);
}
void loop() {
if (! bmp.performReading()) {
Serial.println("Failed to perform reading :(");
return;
}
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(bmp.temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(bmp.pressure / 100.0);
Serial.println(" hPa");
Serial.print("Approx. Altitude = ");
Serial.print(bmp.readAltitude(SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA));
Serial.println(" m");
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor and you should see something like this, the value swill be slightly different depending on your location and current weather conditions
BMP388 test
Temperature = 23.64 *C
Pressure = 844.40 hPa
Approx. Altitude = 470.89 m



Uhm, you send data through serial monitor. Why an ESP8266?
Low cost, easy to use and its easy to do. You can use the wifi capabilities but these examples are to look at various sensors, make sure they work and just give a little easy example of usage.