In this article we will connect a BME680 sensor to an ESP8266 – as usual we will use a Wemos Mini
BME680 is an integrated environmental sensor developed specifically for mobile applications and wearables where size and low power consumption are key requirements. Expanding Bosch Sensortec’s existing family of environmental sensors, the BME680 integrates for the first time high-linearity and high-accuracy gas, pressure, humidity and temperature sensors. The gas sensor within the BME680 can detect a broad range of gases to measure air quality for personal well being.
This was the particular sensor that I used – there are a couple of different modules available
Gases that can be detected by the BME680 include Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) from paints (such as formaldehyde), lacquers, paint strippers, cleaning supplies, furnishings, office equipment, glues, adhesives and alcohol.
| Parameter | Technical data |
|---|---|
| Package dimensions | 8-Pin LGA with metal 3.0 x 3.0 x 0.93 mm³ |
| Operation range (full accuracy) | Pressure: 300…1100 hPa Humidity 0…100% Temperature: -40…85°C |
| Supply voltage VDDIO Supply voltage VDD |
1.2 … 3.6 V 1.71 … 3.6 V |
| Interface | I²C and SPI |
| Average current consumption (1Hz data refresh rate) |
2.1 µA at 1 Hz humidity and temperature 3.1 µA at 1 Hz pressure and temperature 3.7 µA at 1 Hz humidity, pressure and temperature 0.09‒12 mA for p/h/T/gas depending on operation mode |
| Average current consumption in sleep mode | 0.15 μA |
| Gas sensor Response time (τ 33-63%) Sensor-to-sensor deviation Power consumption Output data processing |
< 1 s (for new sensors) +/- 15% +/- 15 < 0.1 mA in ultra-low power mode direct output of IAQ: Index for Air Quality |
| Humidity sensor Response time (τ0-63%) Accuracy tolerance Hysteresis |
8 s ± 3 % relative humidity ≤ 1.5 % relative humidity |
| Pressure sensor RMS Noise Sensitivity Error Temperature coefficient offset |
0.12 Pa (equiv. to 1.7 cm) ± 0.25 % (equiv. to 1 m at 400 m height change) ±1.3 Pa/K (equiv. to ±10.9 cm at 1°C temperature change) |
Parts List
Here are the parts I used
| Name | Links | |
| Wemos Mini | ||
| BME680 | ||
| Connecting cables |
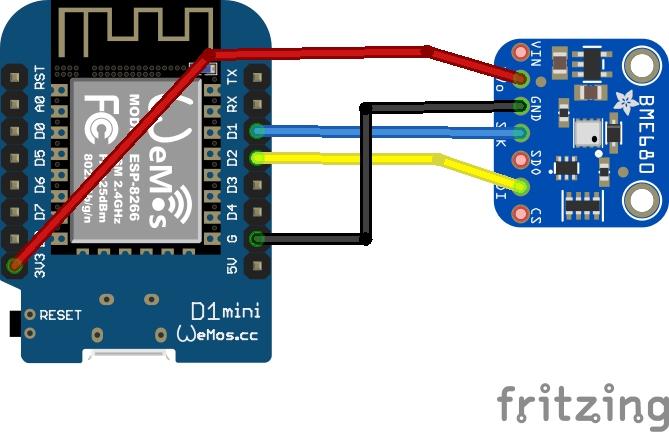
Schematic
We use the I2C connection for the sensor
Code
You will need to import the adafruit sensor and bme680 libraries – you can add these using the library manager
My particular sensor used address 0x76, the default is 0x77 so you may have to change this line from if (!bme.begin(0x76)) to if (!bme.begin())
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include "Adafruit_BME680.h"
#define SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA (1013.25)
Adafruit_BME680 bme; // I2C
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial);
Serial.println(F("BME680 test"));
if (!bme.begin(0x76))
{
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BME680 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
// Set up oversampling and filter initialization
bme.setTemperatureOversampling(BME680_OS_8X);
bme.setHumidityOversampling(BME680_OS_2X);
bme.setPressureOversampling(BME680_OS_4X);
bme.setIIRFilterSize(BME680_FILTER_SIZE_3);
bme.setGasHeater(320, 150); // 320*C for 150 ms
}
void loop()
{
if (! bme.performReading())
{
Serial.println("Failed to perform reading :(");
return;
}
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(bme.temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
Serial.print("Pressure = ");
Serial.print(bme.pressure / 100.0);
Serial.println(" hPa");
Serial.print("Humidity = ");
Serial.print(bme.humidity);
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Gas = ");
Serial.print(bme.gas_resistance / 1000.0);
Serial.println(" KOhms");
Serial.print("Approx. Altitude = ");
Serial.print(bme.readAltitude(SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA));
Serial.println(" m");
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
}
Output
Open the serial monitor and you will see something like this
Temperature = 23.89 *C
Pressure = 973.94 hPa
Humidity = 41.07 %
Gas = 143.28 KOhms
Approx. Altitude = 332.55 m
Temperature = 24.05 *C
Pressure = 973.88 hPa
Humidity = 40.96 %
Gas = 146.54 KOhms
Approx. Altitude = 332.72 m
Temperature = 24.04 *C
Pressure = 973.94 hPa
Humidity = 40.83 %
Gas = 151.31 KOhms
Approx. Altitude = 332.37 m



why are you using wire.h library in bme680 with esp8266 code is you are using spi configuration(assuming this as you are including spi library)? wire.h is used in i2c communication where we have to define the sda and sck wires in void setup.
Removed the SPI defines but forgot to remove the include for the spi header
Also, of you are including wire library for i2c protocol, then don’t you have to use wire.beginTransmission() and other similar commands for starting communication between master and slave devices (esp8266 & bme680) in this case??
i always try this code then i cant always check wiring
i follow your code but fail.
My particular sensor used address 0x76, the default is 0x77 so you may have to change this line from if (!bme.begin(0x76)) to if (!bme.begin())
please help me to be clear explanation
Missed this – the library in the example is expecting an I2C address of 0x77 as default but my particular sensor used 0x76 so I have to hardcode that value in the sketch. The easiest way to check is to wire up your sensor and load in an I2C Scanner sketch into the Arduino IDE. Basically that goes through a list of addresses and checks if there is any device attached, a quick and easy way to check if everything works and see the address.